Azure Managed Identity Link to heading
Azure Managed Identity is a feature that provides an Azure resource with an automatically managed identity in Azure Active Directory. It eliminates the need for developers to manage credentials, and simplifies the authentication process for users.
Azure Managed Identity can be used with various Azure services, such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Functions, and Azure App Service. It helps to authenticate the application to access other Azure resources, such as Azure Key Vault, Microsoft Azure SQL DB, Azure PostgreSQL server, without requiring the developer to manage credentials.
Azure Managed Identity works by creating an identity for the Azure resource in Azure Active Directory. The identity can be used to authenticate the Azure resource with other Azure services that support Azure Active Directory authentication.
Configuring AAD on PostgreSQL server Link to heading
Step 1: Add App Registration for your PostgreSQL server Link to heading
The first step is to add an app registration for your PostgreSQL server. You can do this using either Powershell or Bash.
Powershell
Connect-AzureAD -TenantId <customer tenant id>
New-AzureADServicePrincipal -AppId 5657e26c-cc92-45d9-bc47-9da6cfdb4ed9
Bash
az login
az ad sp create --id 5657e26c-cc92-45d9-bc47-9da6cfdb4ed9
Step 2: Create a new Azure PostgreSQL flexible server with AAD authentication Link to heading
Once you have created the app registration, you can create a new Azure PostgreSQL flexible server with AAD authentication. This is a simple process that can be completed by following the instructions in the Azure portal.
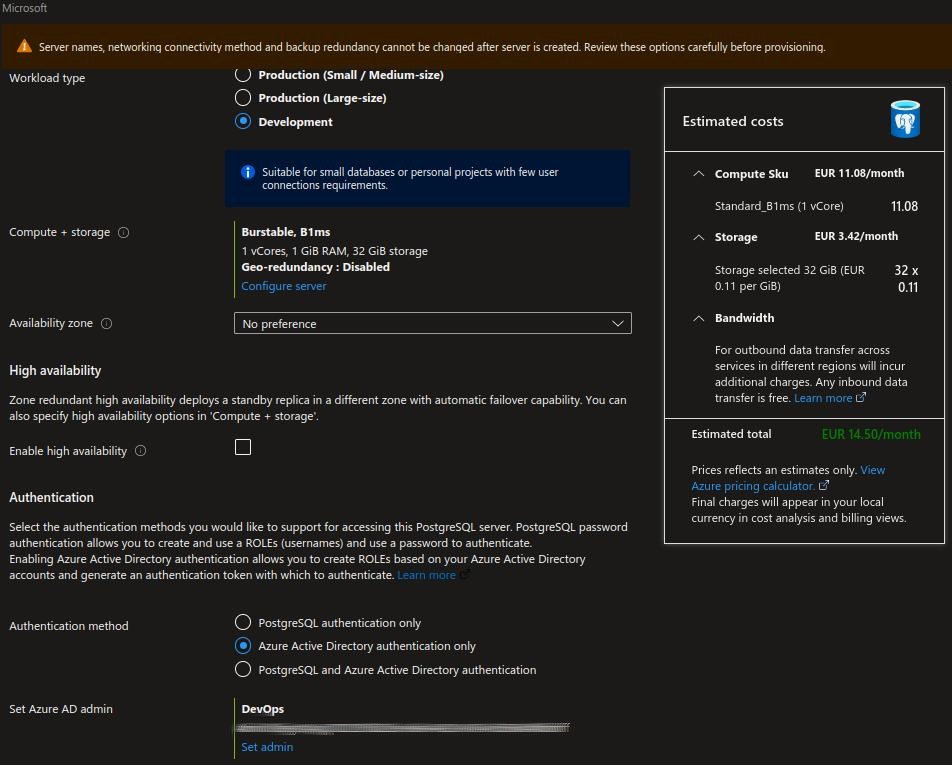
Step 3: Create a user and service principle Link to heading
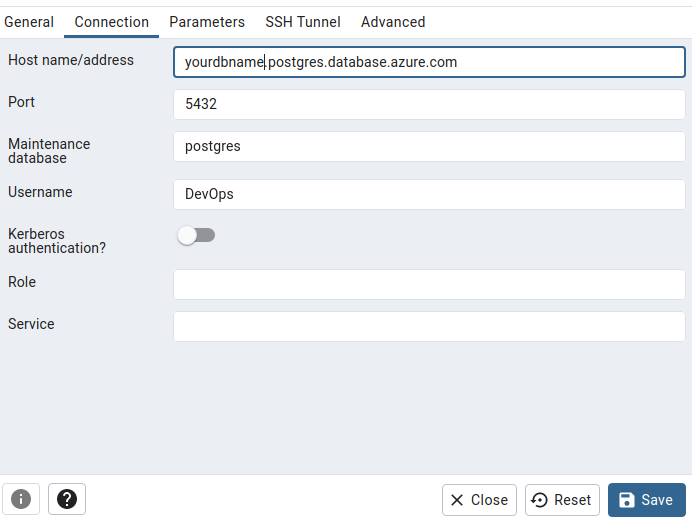
To log in to your new PostgreSQL database, you can use pgAdmin. You will need to fill out the settings as follows:
In the general tab, fill out the Name field with any name and uncheck Connect now.
In the connection tab, use the following settings:
- host name/address:
<nameofyourdb>.postgres.database.azure.com - Username:
group name or aad userin our example DevOps - Parameters: set SSL mode to
Require
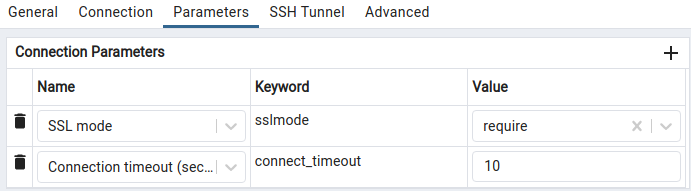
Now, to connect to your database, you will need an access token for your user, who must be a member of your group. You can obtain this access token by running the following command:
az account get-access-token --resource https://ossrdbms-aad.database.windows.net -o json
To create a new admin user in our database can be done by running this SQL script
select * from pgaadauth_create_principal('dewa@contoso.com', true, false);
Here, true will create admin user, and false will return not enable multi-factor authentication.
To create a new service principal user in our database can be done by running this SQL script
select * from pgaadauth_create_principal_with_oid('accounting_application', '00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000', 'service', false, false);
Here, the roleName is the name of the role to be created, objectId is the unique object identifier of the Azure AD object, objectType is the type of the Azure AD object to link to this role, isAdmin should be set to true when creating an admin user and false for a regular user, and isMfa is a flag indicating whether Multi Factor Authentication must be enforced for this role.
Step 4: List Azure AD roles using SQL script Link to heading
After creating your roles and users, you can list Azure AD roles using the following SQL script:
select * from pgaadauth_list_principals(true);
Here, true will return admin users, and false will return all AAD users, including both AAD admins and non-AAD admins.
For more information on managing Azure AD users on PostgreSQL flexible server, you can refer to the official documentation available at https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/postgresql/flexible-server/how-to-manage-azure-ad-users.
In conclusion, configuring AAD on PostgreSQL server involves a few steps that can be executed using either PowerShell or Bash. Once we have added app registration for the PostgreSQL flexible server, we can create new Azure PostgreSQL flexible server with AAD authentication. Then, we can create users and service principal and connect to our database using pgAdmin. Finally, we can list Azure AD roles using SQL scripts. By following these steps, we can enable AAD authentication on our PostgreSQL server and enhance the security of our database.